Angular Form Validation Example Tutorial
Angular 4 Form Validation Example Tutorial
Angular Form Validation Example Tutorial is today’s topic. Angular is a platform that makes it easy to build applications with the web. Angular combines declarative templates, dependency injection, an end to end tooling, and integrated best practices to solve development challenges. User actions such as clicking a link, pushing a button, and entering text raise DOM events. Forms are the mainstay of business applications. You use forms to log in, submit a help request, place an order, book a flight, schedule a meeting, and perform countless other data-entry tasks. Improve overall data quality by validating user input for accuracy and completeness.
Angular Form Validation Tutorial
You can find the full Angular Validation docs on this URL:
We are using Angular Reactive Validation Form.
Step 1: Make one Angular Project.
Install Angular globally by the following command.
npm install -g @angular/cli
After that, type the following command to make a project.
ng new ngValidation
Create some files and also install all the dependencies related project.
Next, go to the project root and type the following command to start the server and open the project.
cd my-app
ng serve --openStep 2: Make one form inside app.component.html
We are going to create a form with one input for just basic understanding for Angular Forms.
First, we need to include Reactive Form in app.module.ts file.
// app.module.ts
import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
imports: [
BrowserModule, ReactiveFormsModule
],
Now, we need to write the code to display the form.
<!--The whole content below can be removed with the new code.-->
<div style="text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}!!
</h1>
<form [formGroup]="angForm" novalidate>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="center-block">Name:
<input class="form-control" formControlName="name">
</label>
</div>
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['name'].invalid && (angForm.controls['name'].dirty || angForm.controls['name'].touched)" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['name'].errors.required">
Name is required.
</div>
</div>
</form>
<p>Form value: {{ angForm.value | json }}</p>
<p>Form status: {{ angForm.status | json }}</p>
</div>
Also, we need to update the app.component.ts file.
// app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormBuilder, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular Form Validation Tutorial';
angForm: FormGroup;
constructor(private fb: FormBuilder) {
this.createForm();
}
createForm() {
this.angForm = this.fb.group({
name: ['', Validators.required ]
});
}
}
I am going to explain how it is working so bear with me.
Step 3: Explanation
There are two types of forms in Angular.
- Template Driven Forms
- Reactive Forms
Template Driven Forms
In this kind of form, we can write the forms in Angular template syntax with form syntax directives.
Following are the steps to build template driven forms.
- Create the component that controls the form.
- Create a template with the initial form layout.
- Bind data properties to each form control using the two-way data-binding syntax.
- Add an attribute to each form-input control.
- Add custom CSS to provide visual feedback.
- Show and hide validation-error messages.
- Handle form submission with ngSubmit.
- Disable the form’s Submit button until the form is valid.
Reactive Forms
We have used Reactive Forms in our example in this article.
Reactive forms is an Angular technique for creating forms in a reactive style. Angular reactive forms facilitate a reactive style of programming that favors explicit management of the data flowing between a non-UI data model (typically retrieved from a server) and a UI-oriented form model that retains the states and values of the HTML controls on the screen. Reactive forms offer the ease of using reactive patterns, testing, and validation.
Example
// app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormBuilder, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular Form Validation Tutorial';
angForm: FormGroup;
constructor(private fb: FormBuilder) {
this.createForm();
}
createForm() {
this.angForm = this.fb.group({
name: ['', Validators.required ]
});
}
}
First, we need to import some of the modules from the @angular/forms.
- FormGroup
- FormBuilder
- Validators
Also, we need have imported ReactiveFormsModule in app.module.ts file.
Then, we have taken heroForm of the type of FormGroup.
Then, we have taken heroForm of the type of FormGroup.
// app.component.ts
constructor(private fb: FormBuilder) {
this.createForm();
}
We have used form builder to handle all the validation. So in that constructor, we are creating a form with the validation rules.
// app.component.ts
createForm() {
this.angForm = this.fb.group({
name: ['', Validators.required ]
});
}
In this code, I have assigned the Validation rules to the Form Object.
<form [formGroup]="angForm" novalidate>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="center-block">Name:
<input class="form-control" formControlName="name">
</label>
</div>
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['name'].invalid && (angForm.controls['name'].dirty || angForm.controls['name'].touched)" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['name'].errors.required">
Name is required.
</div>
</div>
</form>
<p>Form value: {{ angForm.value | json }}</p>
<p>Form status: {{ angForm.status | json }}</p>
In this HTML code, I have assigned the global form group object called angForm. This is the top-level object.
All the inner form controls are like the children to them. We can also access its values.
I have used the conditional statement, if a user has touched the input field but not enter the values then, it displays the message. If user blurs the input field without any values then also it gives an error message.
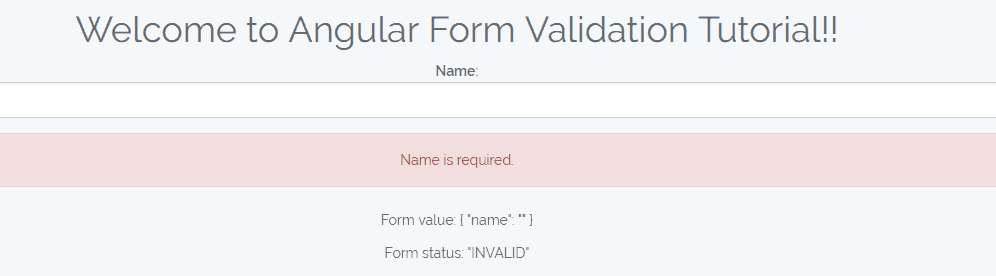
Step 5: Complete Form And Its Code
I am writing important files.
<!-- app.component.html -->
<div class="container">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}!!
</h1>
<form [formGroup]="angForm" novalidate>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Name:</label>
<input class="form-control" formControlName="name" type="text">
</div>
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['name'].invalid && (angForm.controls['name'].dirty || angForm.controls['name'].touched)" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['name'].errors.required">
Name is required.
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Address:</label>
<input class="form-control" formControlName="address" type="text">
</div>
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['address'].invalid && (angForm.controls['address'].dirty || angForm.controls['address'].touched)" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="angForm.controls['email'].errors.required">
email is required.
</div>
</div>
<button type="submit"
[disabled]="angForm.pristine || angForm.invalid" class="btn btn-success">
Save
</button>
</form>
<br />
<p>Form value: {{ angForm.value | json }}</p>
<p>Form status: {{ angForm.status | json }}</p>
</div>
app.component.ts file looks like this.
// app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormBuilder, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular Form Validation Tutorial';
angForm: FormGroup;
constructor(private fb: FormBuilder) {
this.createForm();
}
createForm() {
this.angForm = this.fb.group({
name: ['', Validators.required ],
address: ['', Validators.required ]
});
}
}
This is it for Angular Form Validation article.

0 comments:
Post a Comment