Mapping Relational Databases to MongoDB
If you are coming from a relational database background then it might be difficult for you to relate the RDBMS terms with MongoDB. In this guide, we will see the mapping between relational database and MongoDB.
Mapping relational database to MongoDB
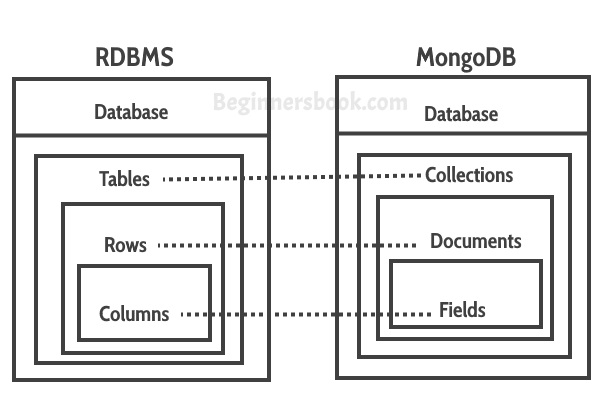
Collections in MongoDB is equivalent to the tables in RDBMS.
Documents in MongoDB is equivalent to the rows in RDBMS.
Fields in MongoDB is equivalent to the columns in RDBMS.
Fields (key and value pairs) are stored in document, documents are stored in collection and collections are stored in database.
This is how a document looks in MongoDB: As you can see this is similar to the row in RDBMS. The only difference is that they are in JSON format.
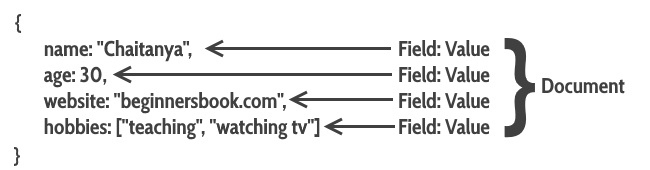 Table vs Collection
Table vs Collection
 Table vs Collection
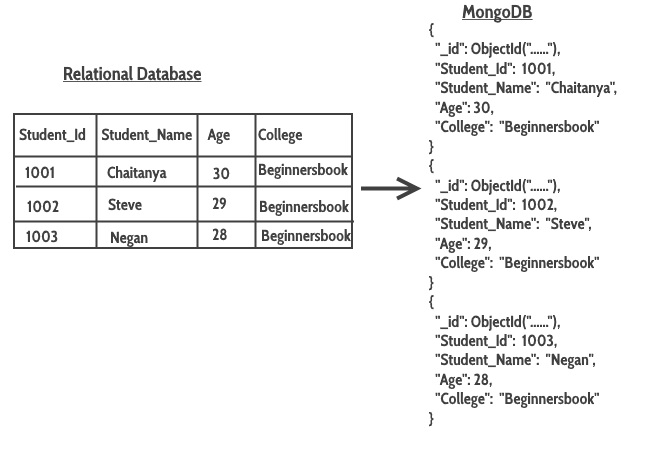
Table vs CollectionHere we will see how a table in relational database looks in MongoDB. As you see columns are represented as key-value pairs(JSON Format), rows are represented as documents. MongoDB automatically inserts a unique _id(12-byte field) field in every document, this serves as primary key for each document.
Another cool thing about MongoDB is that it supports dynamic schema which means one document of a collection can have 4 fields while the other document has only 3 fields. This is not possible in relational database.

Another cool thing about MongoDB is that it supports dynamic schema which means one document of a collection can have 4 fields while the other document has only 3 fields. This is not possible in relational database.

0 comments:
Post a Comment