Angular 2 interview questions
Below are the list of Angular 2 interview questions that have been designed for Angular 2 programmers who are preparing interviews on Angular2 interviews. Here, we have added some basic and advanced or both questions on Angular 2 that are asked in 2017 and help you to crack interview on Angular 2.
You can also download latest Angular2 interview questions and answers pdf for freshers and experienced.
You can also download latest Angular2 interview questions and answers pdf for freshers and experienced.
Top 34 Angular 2 interview questions and answers.
- What is Angular 2?
- List some advantages of Angular 2 over Angular1?
- What are the new features of Angular 2?
- How do you define the transition between two states in Angular?
- How to declare a component in Angular 2?
- What is the difference between observable and promises?
- List the differences between Angular 2 components vs. directives?
- What is ECMAScript?
- What is Traceur Compiler?
- List the modern browsers supported by Angular 2?
- When to use Ngoninit and constructor in Angular 2?
- How to cache an observable data?
- List out the differences between ActivatedRoute and RouterState, with reference to Angular 2.
- What would you have in a shared module in Angular 2?
- What do you mean by a structural directive in Angular 2?
- What do you understand by a template variable? How is it used?
- Explain the concept of lazy loading in Angular 2.
- What is the difference between constructor and ngOnlnit in Angular js?
- What is the meaning of component life cycle in Angular 2?
- What is the use of ngForTrackBy directive?
2. What is Advantages of Angular 2?
There is many more advantage of Angular 2.
1. The Angular 2 has better performance.
2. The Angular 2 has more powerful template system.
3. The Angular 2 provide simpler APIs, lazy loading and easier to application debugging.
4. The Angular 2 much more testable.
5. The Angular 2 provides to nested level components.
6. The Angular 2 execute run more than two programs at the same time.
7. Angular1 is controllers and $scope based but Angular2 is component based.
8. The Angular2 structural directives syntax is changed like
9. In Angular2, local variables are defined using prefix
2. The Angular 2 has more powerful template system.
3. The Angular 2 provide simpler APIs, lazy loading and easier to application debugging.
4. The Angular 2 much more testable.
5. The Angular 2 provides to nested level components.
6. The Angular 2 execute run more than two programs at the same time.
7. Angular1 is controllers and $scope based but Angular2 is component based.
8. The Angular2 structural directives syntax is changed like
ng-repeat is replaced with *ngForetc.9. In Angular2, local variables are defined using prefix
(#) hash.
The Angular 2 architecture diagram identifies the eight main building blocks as.
1. Module
2. Component
3. Template
4. Outpouts
5. Data Binding
6. Directive
7. Service
8. Dependency Injection
2. Component
3. Template
4. Outpouts
5. Data Binding
6. Directive
7. Service
8. Dependency Injection
The Angular 2 framework consists of several libraries, the some of them working as core and some are optional.
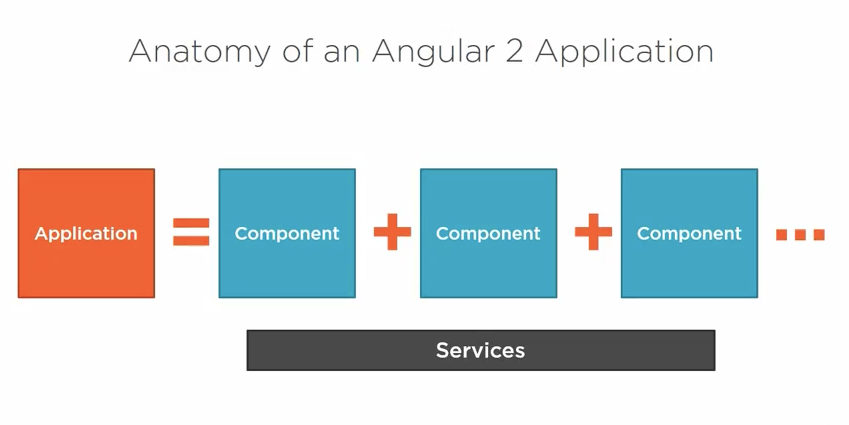
3. What is the anatomy of angular 2 application?
An application is consists of a set of components, and some services, each component is comprised of a template,Classes and metadata (look to the following figure ).
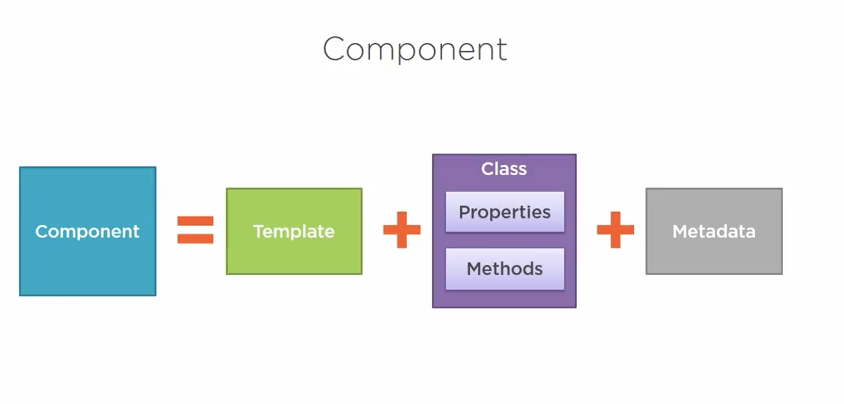
4. what is an Angular 2 component?
In Angular 2, “everything is a component.” Components are the main way we build and specify elements and logic on the page, through both custom elements and attributes that add functionality to our existing components.
Each component is comprised of a template, which is the HTML for the user interface. Add to that a class for the code associated with a view. The class contains the properties and methods, which perform actions for the view,A component also has metadata, which provides additional information about the component to Angular.
5. Can we write both Angular 1 and Angular 2 codes in a single project?
1. Angular frameworks provide the support of mixing code of Angular 1 and Angular 2 in the same application.
2. We can write the mixing components of Angular 1 and Angular 2 in the same view.
3. We can inject services across frameworks of Angular 1 and Angular 2 in the same application.
4. Both Angular 1's and Angular 2's data binding works across frameworks in the same view.
2. We can write the mixing components of Angular 1 and Angular 2 in the same view.
3. We can inject services across frameworks of Angular 1 and Angular 2 in the same application.
4. Both Angular 1's and Angular 2's data binding works across frameworks in the same view.
6. What is the languages that you can use to build angular 2 application?
* ECMAScript, or ES.
–ES 3 is supported by older browsers.
–ES 5 is the version currently supported by most modern browsers.
–The ES 6 specification was recently approved and renamed ES 2015(Most browsers don't yet support ES 2015).
–ES 5 is the version currently supported by most modern browsers.
–The ES 6 specification was recently approved and renamed ES 2015(Most browsers don't yet support ES 2015).
* TypeScript
–TypeScript is the superset of JavaScript and must be transpiled.
–TypeScript has great tooling
–Inline documentation.
– Syntax checking.
– Code navigation.
– Advanced refactorings.
–TypeScript has great tooling
–Inline documentation.
– Syntax checking.
– Code navigation.
– Advanced refactorings.
7. What is ECMAScript ES5/ES6?
The ECMAScript is a scripting language which is developed by Ecma International Org.
Currently ECMAScript available in multiple versions that are ES5 and ES6 and both of versions fully supported to Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Safari, and IE etc.
8. What is Traceur compiler?
The Traceur is a JavaScript compiler. The Traceur compiler is very popular now days use to allow use to use the features from the future. This compiler is fully supported to ES5, ES6 and also to vNext.
The main goal of Traceur compiler is to inform to design of new JavaScript features and wrote the programming code of new efficient and good manners.
9. Differentiate between Angular 2 Component Constructor vs. OnInit event?
The
constructor is a typescript feature. The constructor is only related to class instantiation and it’s nothing to do with Angular 2 and it is use to some initialization processing with respect to class hierarchies for the newly created instance.
The
ngOnInit event is an Angular 2 life-cycle event/ method that are called after the first ngOnChanges. The ngOnInit method is use to parameters defined with @Input otherwise the constructor is OK.
10. What is Angular 2 Components Life cycle?
In Angular 2 components life-cycle, there are several events occur to complete this life-cycle.
| Events | Description |
|---|---|
| ngOnChanges | Before Ng on init event, the data-bound input property value changes. |
| ngOnInit | After the first ngOnChanges event, the ngOnInit event fire. |
| ngDoCheck | During every Angular change detection cycle ngDoCheck event fire. |
| ngAfterContentInit | After projecting content into the component ngAfterContentInit event fire. |
| IngAfterContentChecked | After every check of projected component content the ngAfterContentChecked event fire. |
| ngAfterViewInit | After initializing the component's views and child views the ngAfterViewInit event fire. |
| ngAfterViewChecked | After every check of the component's views and child views the ngAfterViewChecked event fire. |
| ngOnDestroy | Just before Angular destroys the directive or component the ngOnDestroy event fire. |
11. What is Angular 2 Directives?
* Angular 2 directives meta-data annotation is used to register the directives.
* The directives are used to add behaviour to existing DOM elements.
* The directives are used to design a reusable component.
* More than one directive is used per DOM element.
* The directive does not have @View etc.
* The directives are used to add behaviour to existing DOM elements.
* The directives are used to design a reusable component.
* More than one directive is used per DOM element.
* The directive does not have @View etc.
Example
import {Component, View} from 'angular2/core'';
@Component({
selector: 'user-detail'
})
@View({
template: "<div> <h1>{{userName}}</h1> <p>{{phone}}</p>"
})
class userDetail {
constructor(public userName: string, public phone: string) {}
}
<user-detail></user-detail></div>
12. What is Angular 2 Template?
A template is a HTML view that tells Angular 2, how to render your components in the views. The Angular 2 templates are very similar to Angular 1 but Angular 2 have some small syntactical changes.
You can see the changes as below
* {}: Is use to rendering the HTML elements.
* []: Is use to binding properties.
* (): Is use to handling your events.
* [()]: Is use to data binding.
* *: Is use to asterisk Operations like *ngFor="#item of items”
* []: Is use to binding properties.
* (): Is use to handling your events.
* [()]: Is use to data binding.
* *: Is use to asterisk Operations like *ngFor="#item of items”
13. Differentiate between Angular 2 components vs directives?
Angular 2 components vs directives
| @Components | @Directive |
|---|---|
| @Component meta-data annotation is used to register the components. | @Directive meta-data annotation is used to register the directives. |
| The components are used to create UI widgets. | The directives are used to add behavior to existing DOM elements. |
| The components are used to split to application into smaller parts. | The directives are use to design a reusable components. |
| Only one component is used per DOM element. | More than one directive are used per DOM element. |
| In the components, @View, template and templateUrl are mandatory in the components. | The directive do not have @View etc. |
Example for using Component:
import {Component, View} from 'angular2/core';
@Component({
selector: 'hello-world'
})
@View({
template: "<h1>Hello {{angular}}</h1>"
})
class hello {
constructor(public angular: string) {}
}
<hello-world></hello-world>
Example for using Directive:
import {Component, View} from 'angular2/core'';
@Component({
selector: 'user-detail'
})
@View({
template: "<div> <h1>{{userName}}</h1> <p>{{phone}}</p>"
})
class userDetail {
constructor(public userName: string, public phone: string) {}
}
<user-detail></user-detail>
14. What is Angular 2 @Inputs?
Angular 2 component is the core components of applications but we need to know how to pass data into components to dynamically.
For the same, we need to define an input (use like @Input decorator) for a component.
How to pass data into components? We can see the below example for passing the user data in to the components.
For Example,
import { Component, Input } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: “user-info”,
template: “<div> Hello, This is {{ userInfo.name}}</div>”
})
export class UserInfo {
@Input() userInfo;
constructor() { }
}
<user-info [userInfo]="currentUser"></user-info>
The components is use to render the user information on the view.
15. What is Angular 2 Outputs?
In Angular 2, if we want to bind an event on an element, we can use the new Angular 2 events i.e.
<button (click)="addUser()">Click</button>
The method
addUser() will be called when user clicked on button.
16. What happen if you want to create a custom event?
Now come to the outputs, if we want to create our custom event in Angular 2 that time we will use to new @Output decorator.
Example
import { Component} from 'angular2/core';
import { bootstrap} from 'angular2/platform/browser';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
providers: [Service],
template: '<div>Hello my name is {{name}}!</div>'
})
class MyApp {
constructor(service: Service) {
this.name = service.getName();
setTimeout(() => this.name = 'Saurabh Samir,', 1000);
}
}
class Service {
getName() {
return 'Hello';
}
}
bootstrap(App);
In the above example, we will need to import Output and Event-Emitter to create our new custom event.
import { Component , Output, EventEmitter} from 'angular2/core';
import { bootstrap} from 'angular2/platform/browser';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
providers: [Service],
template: '<div>Hello my name is {{name}}!</div>'
})
class MyApp {
constructor(service: Service) {
this.userClicked.emit(this.user);
this.name = service.getName();
setTimeout(() => this.name = 'Saurabh Samir,', 1000);
}
}
class Service {
getName() {
return 'Hello';
}
@Output() userClicked = new EventEmitter();
}
bootstrap(App);
Now when we are using the components anywhere in our application, we can bind the our custom event i.e.
<my-app (userclicked)="userClicked($event)"></my-app>
17. What is Angular 2 components css styles and styleUrls?
The Angular 2 components styling can be
1.Inline styles
2.CSS Style URLs and
3.Template inline styles
2.CSS Style URLs and
3.Template inline styles
The Angular 2 components allow us to define both type of css that are inline css and styleUrls and the detail about it as given below.
Components Inline CSS Styles
@Component({
selector: 'customers',
templateUrl: 'customers.html',
styles: [
.customer {
padding:0.3em;
background-color: #f5f5f;
box-shadow: inset 1px 1px 1px rgba(0,0,1,0.2);
border-radius:1px;
border: solid 1px #c1c1c;
}]
})
Components CSS styleUrls
@Component({
selector: 'customers',
templateUrl: 'customers.html',
styleUrls: ['customers.css']
})
//customers.css
.customer {
padding:0.3em;
background-color: #f5f5f;
box-shadow: inset 1px 1px 1px rgba(0,0,1,0.2);
border-radius:1px;
border: solid 1px #c1c1c;
}
Components Template inline css styles
<style>
.customer {
padding:0.3em;
background-color: #f5f5f;
box-shadow: inset 1px 1px 1px rgba(0,0,1,0.2);
border-radius:1px;
border: solid 1px #c1c1c;
}
</style>
<div class="customer">
<div (click)="toggle()">
{{IsVisible ? true : false }} {{CustomerUID}}
</div>
<div [hidden]="!IsVisible">
<customer></customer>
</div>
</div>
18. What is ECMAScript ES6/ES7? Breifly explain both. Which version is supported by Angularjs 2.
ECMAScript is a standard for modern scripting-language specification. Initially, it was JavaScript, now its being changing to ECMAScript.
6th Edition – ECMAScript 2015:
ECMAScript 2015 is the 6th Edition. This version has significant contribution for:
* Class Inheritance
* Iterators for loop
* Python-style generators and generator expressions
* Advanced set for collections
* number and math enhancements
* Promises
* Metaprogramming for virtual objects and wrappers and so on.
* Iterators for loop
* Python-style generators and generator expressions
* Advanced set for collections
* number and math enhancements
* Promises
* Metaprogramming for virtual objects and wrappers and so on.
Although, ES6 still does not support browser. Therefore, compiler such as Traceur are required to compile EC6 code to pure javascript on the fly in browser.
7th Edition – ECMAScript 2016:
The 7th edition, officially known as ECMAScript 2016, has been finalized in June 2016.
Which version is supported by Angular2?
Angular has used 6th Edition – ECMAScript 2015 (Es6). However, there are configuration available to try some experimental feature from 7th Edition – ECMAScript 2016 (Es7).
Inheritance of component has become so easy. Now Angular 2.0 can be developed using Object oriented thinking. Inheritance has been possible for javascript. A number of libraries has been developed to support this concept. However, with ES2015 all those nonstandard abstractions can be got rid of. As ES2015 defines an easier inheritance.
19. Angular 2 toggle button?
Syntax:
<button (click)="toggle()">Toggle Button</button>
//The Example for Angular2 Toggle as given below!
//Step-1
//Import root component.
import {Component, View, CORE_DIRECTIVES} from 'angular2/angular2'
//Step-2
//Component
@Component({
selector: 'toggle-app',
bindings: []
})
//Step-3
//View template.
@View({
template: `
<div>
<button (click)="toggle()">Toggle Button</button>
</div>
<div class="border">
<div *ng-if="isActive">
<h1>Hello Angular 2, Toggle Button.</h1>
</div>
</div>
<p>Status(isActive): {{isActive}}</p>
`,
directives: [CORE_DIRECTIVES]
})
//Toggle class App for active and hide div.
export class App {
isActive: bool = true;
toggle() {
this.isActive = !this.isActive;
}
}
20. Angular 2 ngif else expression?
Syntax:
1.<div *ng-if="your-condition">...</div>
2.<div *ngif="your-condition">...</div>
3.<div template="ngIf your-condition">...</div>
4.<template [ngif]="your-condition">
<div>...</div>
</template>
The example as given below.
//Import root component.
import {Component, View, CORE_DIRECTIVES} from 'angular2/angular2'
//Component
@Component({
selector: 'toggle-app',
bindings: []
})
//View template.
@View({
template: `
<div>
<button (click)="toggle()">Toggle Button</button>
</div>
<div class="border">
<div *ng-if="isActive">
<h1>Hello Angular 2, Toggle Button.</h1>
</div>
</div>
<p>Status(isActive): {{isActive}}</p>
`,
directives: [CORE_DIRECTIVES]
})
export class App {
isActive: bool = true;
toggle() {
this.isActive = !this.isActive;
}
}
21. What is Angular 2 RouteParams?
The Route Params :- The route parameter is used to map given URL's parameters based on the rout URLs and It is an optional parameters for that route.
Syntax :-
params : {[key: string]: string}
Example,
@RouteConfig([
{path: '/employ/:id', component: employe, name: 'emp'},
])
Router-outlet directive :- Router-outlet directive is used to render the components for specific location of your applications. Both the template and templateUrl render the components where you use this directive.
Syntax :-
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
Router-link directive :- Router-link directive is used to link a specific parts of your applications.
Syntax :-
<router-link></router-link>
Example,
<a [router-link]="['/AboutMe']">About Me</a>
The Route-Config :- The route config is used to map components to URLs.
Syntax :-
@RouteConfig([
{path: '/', component: Home_Component, as: 'Home'},
{path: '/AboutMe', component: AboutMe_Component, as: 'AboutMe' }
{path: '/ContactMe', component: ContactMe_Component, as: 'ContactMe' }
])
22. What is Angular 2 hidden property?
Angular 2 [hidden] is a special case binding to hidden property.
It is closest cousin of ng-show and ng-hide .
It is more powerful and use to bind any property of elements. Both the ng-show and ng-hide are used to manage the visibility of elements using ng-hide css class. It is also set the display property "display:none".
It is more powerful and use to bind any property of elements. Both the ng-show and ng-hide are used to manage the visibility of elements using ng-hide css class. It is also set the display property "display:none".
All the above features are supported in Angular 2 but added some extra feature like animations etc.
Example for Angular 2
<div [hidden]="!active">
Hello, This is active!
</div>
Example for Angular 1
<div ng-show="active">
Hello, This is active!
</div>
23. What is Angular 2 templateUrl and styleUrls?
Angular 2 templateUrl :- The templateUrl is a function which returns HTML template.Angular 2 styleUrls:- The styleUrls is a component which use to write inline styles, style Urls and template inline style.
The example as given below using templateUrl and styleUrls.
import {Component} from 'angular2/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app'
templateUrl: 'index.html',
styleUrls: ['main_style.css']
})
export class App_Component { }
24. What is Angular 2 events?
Events in Angular 2 use the parentheses notation in templates, and trigger methods in a component’s class. For example, assume we have this component class:
@Component(...)
class MyComponent {
clicked(event) {
}
}
And this template:
<button (click)="clicked()">Click</button>
Our
clicked() method will be called when the button is clicked.
25. How to import css using System import?
Syntax :
System.import('./app/bootstrap/css/boots-trap.css!').then(() => {
System.import('./app/main-app.css!');
});
26. How to Load external css style into Angular 2 components?
The styles or styleUrls should only be used for css rules and It is affect the style of the template elements.
This is the best approaches to add styles directly to the components and the view encapsulation is set per component. It is use for some situations.
An example to add external styles to components.
@Component({
selector: 'app',
templateUrl: 'app/login.html',
styleUrls: [
'app/app.css',
'app/main.css'
],
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None,
})
export class Component {}
27. What is Dependency Injection (DI) in Angular 2?
Angular 2 Dependency Injection consists of three things.
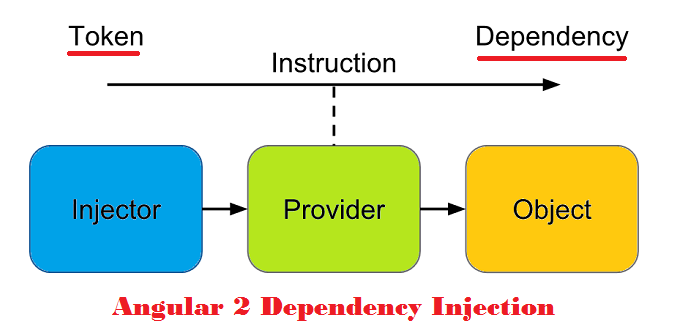
1.Injector
2.Provider
3.Dependency
2.Provider
3.Dependency
Injector :- The injector object use to create instances of dependencies.Provider :- A provider is help to injector for create an instance of a dependency. A provider takes a token and maps that to a factory function that creates an object.Dependency :- A dependency is the type of which an object should be created.
0 comments:
Post a Comment